European Space Agency’s Harmony Mission to Rely on ABB Infrared Instruments
November 13, 2024

- ABB to develop thermal infrared (TIR) imaging instruments for two European Space Agency Harmony satellites, helping the research mission gather new data on Earth’s dynamic systems
- ABB technologies will contribute to the advancement of climate science and the understanding and forecasting of extreme weather events
- Combining thermal and radar imagery enables deeper insights into energy fluxes and exchange processes occurring at the ocean-atmosphere interface
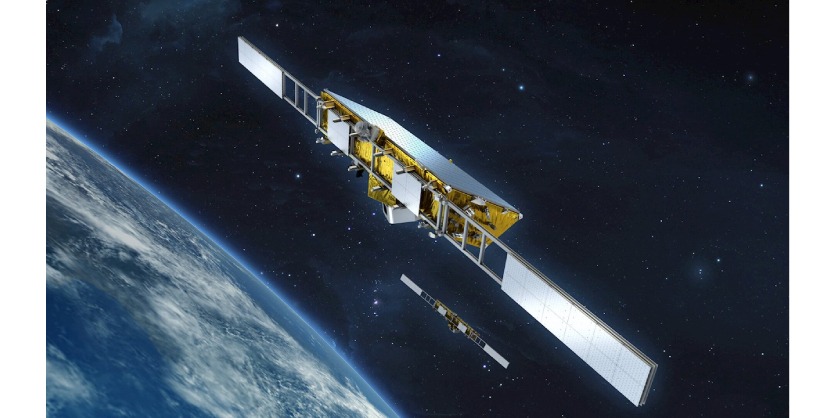
ABB has been selected by the German space and technology company OHB System AG to develop and build the thermal infrared payloads for the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Earth Explorer Harmony satellites, planned to launch in 2029. ABB will equip the two satellites with multispectral thermal infrared payloads capable of measuring a wide range of environmental parameters, including sea surface temperature and the position of clouds and their motion. Financial details were not disclosed.
ABB’s multiview TIR instrument will enable ESA to measure cloud position and motion from space, ensuring radiometric precision – the accuracy of the temperature measurement obtained by the infrared instruments compared to that of the true surface temperature (whether cloud or sea). The data collected by the mission will help the advancement of climate science as well as support the understanding and forecasting of extreme weather such as hurricanes. In addition, over land, Harmony will provide information to estimate small shifts in the shape of the land surface, such as those leading to and resulting from earthquakes and volcanic activity, thereby contributing to the assessment of geohazards over geologically active areas.

“Harmony is poised to further enhance our understanding of how our planet works by delivering valuable data that will benefit Earth system science and climate research,” said Florence Hélière, Harmony Project Manager, European Space Agency. “The expertise and commitment of our industrial partners are invaluable for the Harmony mission, helping us to deliver the mission on time and advance scientific knowledge.”
“We selected ABB on this high-profile mission because of their proven expertise in infrared sensor technologies,” said Agustina Alvarez Toledo, Harmony Project Manager at OHB System AG. “We have been collaborating on several space programs and know that they are very capable. We look forward to working together again to support the scientific community for the benefit of this generation and the ones to follow.”
“ABB’s purpose is to enable a more sustainable and resource efficient future and so we are proud to be a part of this scientific program that will contribute to humanity’s understanding of climate change,” said Jacques Mulbert, President of ABB Measurement & Analytics. “With this work, we are showcasing our ability to provide accurate cloud positioning and sea surface measurement from space, contributing to a deeper scientific understanding of our planet in order to preserve its future.”

The two satellites will orbit the Earth in tandem with a Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellite, the configuration of which will change over the course of Harmony’s life in orbit. In the various configurations, the Harmony satellites’ synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments will receive the Sentinel-1 radar signals that will bounce back from Earth’s surface. At the same time, Harmony’s thermal infrared instruments will provide complementary observations of the sea surface as well as the position and motion of clouds above it.
The combination of thermal and radar imagery will help provide a wide array of data, giving more insight into upper-ocean heat exchanges, drivers of extreme weather, and the long-term impact of climate change. The mission will also provide new information for a better understanding of how ice being lost from glaciers is affecting sea-level rise.
ABB is a global technology leader in electrification and automation, enabling a more sustainable and resource-efficient future. By connecting its engineering and digitalization expertise, ABB helps industries run at high performance, while becoming more efficient, productive and sustainable so they outperform. At ABB, we call this ‘Engineered to Outrun’. The company has over 140 years of history and more than 105,000 employees worldwide. ABB’s shares are listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange (ABBN) and Nasdaq Stockholm (ABB). www.abb.com
Related Story
ABB Technology Helps Make Scientific Discoveries from Space
Recent scientific discoveries reported by the Canadian Space Agency expose a chemical process in the atmosphere through which intense wildfires contribute to ozone layer depletion. These discoveries have been made possible by ABB technology on board the SCISAT satellite.