Hazardous Environment vs. Intrinsically Safe Sensors: Understanding the Differences
April 2, 2025
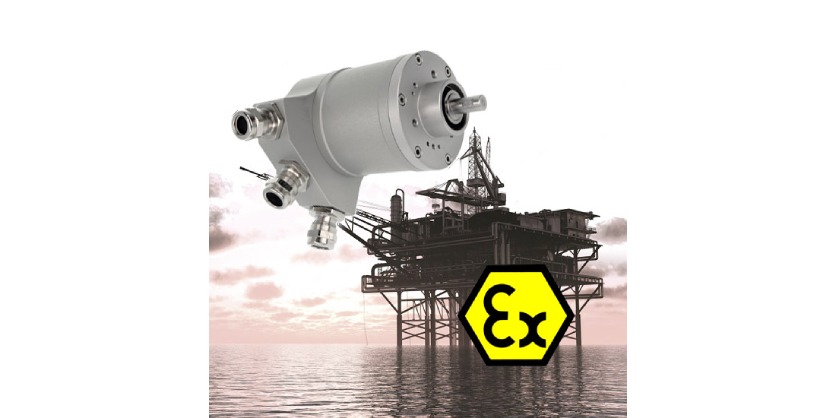

Sensors designed for industrial applications often face harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, high humidity, exposure to chemicals, and the presence of combustible gases or dust.
Two common classifications for sensors used in such environments are hazardous environment sensors and intrinsically safe sensors. While they share some overlap, they serve different purposes and meet distinct safety requirements.
What Are Hazardous Environment Sensors?
Hazardous environment sensors are designed to operate reliably in extreme or potentially dangerous conditions. These sensors are built with durable materials, reinforced enclosures, and protective coatings to withstand physical, chemical, and environmental stresses.
Key Features of Hazardous Environment Sensors
- Durability: Designed to endure mechanical stress, including vibration, shock, and pressure fluctuations.
- Corrosion Resistance: Constructed with materials resistant to chemicals, moisture, and saltwater.
- Temperature Tolerance: Capable of functioning in both high and low-temperature extremes.
- Ingress Protection (IP): Often rated for resistance against dust and water intrusion (e.g., IP67, IP68).
- Explosion Protection: Some hazardous environment sensors are built to contain or prevent ignition sources, but not all fall under this category.
Common Applications
- Oil and Gas Industry: Monitoring pressure, temperature, and flow in pipelines and refineries.
- Chemical Processing: Ensuring safe operations in environments with aggressive chemicals.
- Mining Operations: Detecting gases, structural integrity, and environmental conditions underground.
- Heavy Machinery and Manufacturing: Measuring position, temperature, and load in extreme industrial settings.
What Are Intrinsically Safe Sensors?
Intrinsically safe (IS) sensors are specifically designed to prevent ignition in hazardous areas by limiting the electrical and thermal energy available to a level that cannot ignite flammable gases, dust, or vapors. Instead of containing or isolating ignition sources, intrinsically safe sensors reduce energy output so that even a fault condition will not cause an explosion.
Key Features of Intrinsically Safe Sensors
- Low Power Operation: Designed to function with minimal voltage and current to prevent spark or heat generation.
- Certified for Hazardous Zones: Must meet safety certifications such as ATEX, IECEx, UL, and CSA for use in explosive atmospheres.
- Safety Barriers Required: Often used with intrinsically safe barriers or isolators to limit electrical energy from reaching dangerous levels.
- Minimal Heat Generation: Ensures that even in case of a fault, the sensor will not produce enough heat to ignite flammable substances.
Common Applications
- Oil Refineries and Gas Plants: Used in areas with explosive gas mixtures to prevent ignition.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Monitoring environmental conditions in solvent-heavy production lines.
- Grain Processing and Agriculture: Used in areas where combustible dust is present.
- Underground Mining: Ensuring safe operation in methane-rich environments.
Differences Between Hazardous Environment Sensors and Intrinsically Safe Sensors
| Feature | Hazardous Environment Sensors | Intrinsically Safe Sensors |
|---|
| Purpose | Designed to withstand harsh conditions | Designed to prevent ignition in explosive atmospheres |
| Explosion Protection | May or may not be explosion-proof | Always designed to prevent ignition |
| Energy Limitation | No strict energy limitations | Limits voltage, current, and heat output |
| Physical Protection | Rugged enclosures, corrosion-resistant materials | Safety circuits and isolators to limit energy levels |
| Certifications | Varies by application (IP ratings, corrosion resistance) | Must meet IS standards (ATEX, IECEx, UL, CSA) |
| Applications | Extreme heat, moisture, pressure, chemicals | Explosive gas or dust environments |
When to Use Each Type
- If your environment involves extreme temperatures, pressure, moisture, or corrosive substances but does not have an explosion risk, hazardous environment sensors are a good fit.
- If your application is in an area with flammable gases, vapors, or dust, intrinsically safe sensors are required to prevent potential ignition sources.
Some sensors are both hazardous environment-rated and intrinsically safe, meaning they offer rugged durability while also meeting IS safety requirements.
Choosing between hazardous environment sensors and intrinsically safe sensors depends on the specific risks in your application. Hazardous environment sensors are built for extreme conditions, while intrinsically safe sensors are designed to operate safely in explosive atmospheres by limiting energy output. Understanding these distinctions ensures compliance with safety regulations and protects both personnel and equipment in industrial environments.
Related Story
Ask An Expert at Electromate
If you have questions about any of Electromate’s product offerings, please book a consultation with one of their Sales Engineers in your area. If you just have a question about one of their motion control or robotic lines, simply fill out the Ask an Expert form below. They strive to get you an answer ASAP.