Festo’s Solutions Prevent Contamination in Lithium-Ion EV Batteries
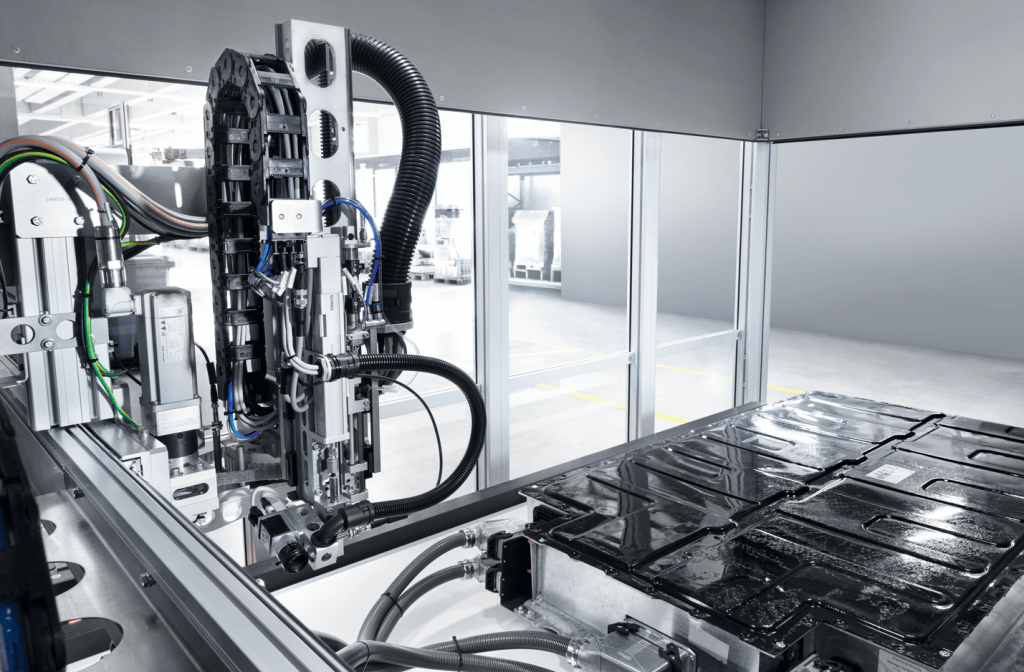
Safe and precise production is critical to ensuring the quality of a battery; any contamination can compromise its performance, lifespan, and safety. Festo is a trusted, single source supplier for all tasks involving automation of battery manufacturing. They offer a complete line of copper-free, zinc-free, and dry-room-compatible components for battery manufacturing.
December 18, 2024
By Krystie Johnston
Today, approximately 95% of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems use conventional lithium-ion batteries, which require liquid electrolyte filling. Lawrence Lin, Business Development Manager at Festo, focuses on supporting the automation of battery production for EVs and energy storage systems. Lin specializes in automation advancements and technologies that drive improvements in productivity, quality, and safety through innovative designs.

Safe and precise production is critical to ensuring the quality of a battery; any contamination can compromise its performance, lifespan, and safety. “During the battery production’s formation stage, any contamination in the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) can lead to electrolyte breakdown during operation, potentially accelerating dendrite growth,” Lin says. “SEI is a thin protective layer that forms on the surface of the anode in lithium-ion batteries during the initial charging cycles, and it directly influences the battery performance, lifespan, and safety.”
Dendrite growth results from interfering metallic particles such as copper, nickel, and zinc that disrupt the crystal structure of the battery cell. These branch-like structures can span the gap between the anode and the cathode, causing electrical shorts and thermal runaway. Lin says they can also diminish the battery’s charge density, degrade the overall performance, and compromise mechanical stability.
“It is critical to prevent particle contamination because it can lead to electrical shorts and thermal runaway. Even the smallest metal particle contamination can create conductive pathways between the anode and cathode layers, causing internal short circuits. These shorts generate excessive heat, which can trigger thermal runaway. The most severe consequence occurs when dendrites reach the battery cell walls, potentially causing the cell to rupture, explode, and ignite a fire.”
These are consequences that need to be avoided for obvious reasons. So, how much of one of these metallic particles constitutes contamination? And how can this be avoided? Lin says that while there are currently no established industry standards for the manufacturing environment of battery cells, the general guideline is to maintain cleanliness equivalent to a Class 100 clean room (ISO 5). For reference, this environment permits a maximum of 100 particles smaller than 0.5 micrometers per cubic foot.
Moreover, Festo goes beyond the normal standard. They developed the Festo Guidelines, which provide a clear procedure for minimizing the risk of contamination by avoiding the use of non-ferrous metals. These guidelines have been established as a company-wide standard for all locations worldwide, ensuring the safe and reliable production of battery cells that ensures greater customer confidence in the product and lower reject rates for the manufacturer. In fact, Festo’s F1A product portfolio was developed specifically for the requirements of battery production.
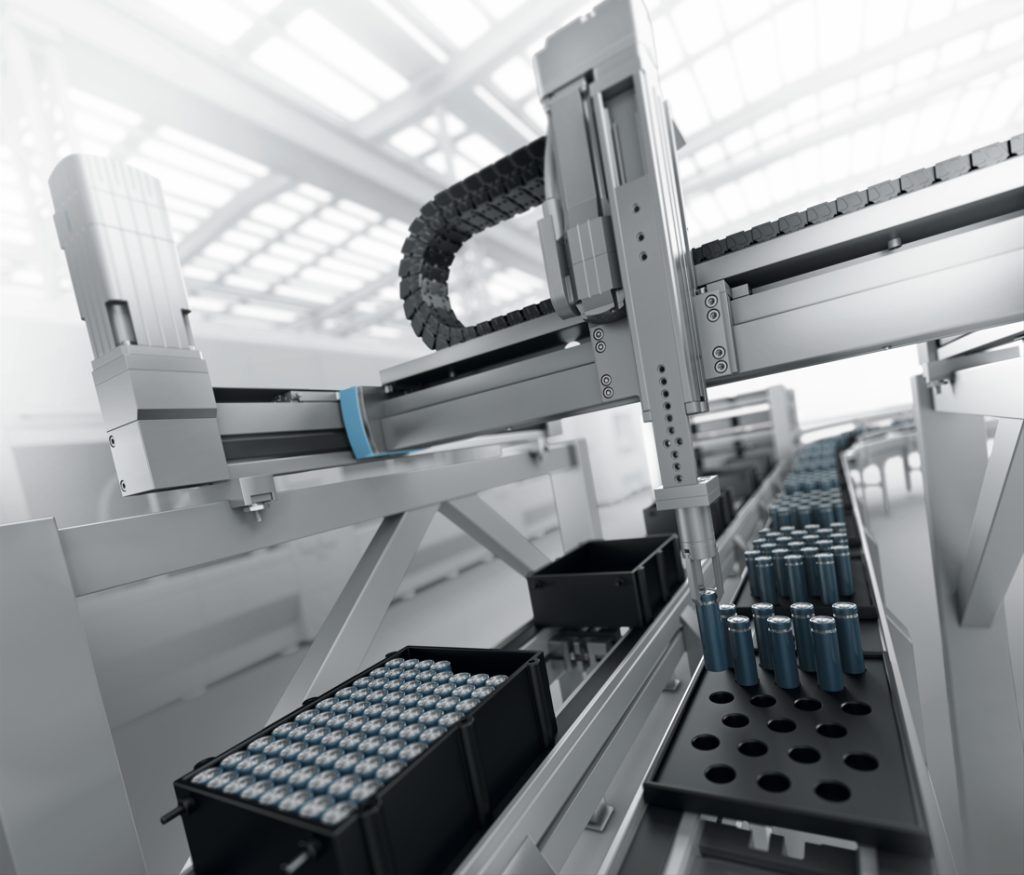

Contamination can occur at any point during the material handling and cell manufacturing process of the anode, separator, and cathode sheets. Lin says there is no single step in this process that is more (or less) susceptible to contamination. For instance, he says that metal shavings from manufacturing equipment are a common source of contamination – even within the cleanroom environment. “The overall cleanliness and use of non-ferrous metal-free components in the cleanroom manufacturing environment plays a critical role in preventing contamination before battery cells are sealed.”
The only way to detect if the battery cell has become contaminated is with ultrasonic testing. Lin says this process helps manufacturers identify problematic cells and sort them before they are assembled into modules for use. “Unfortunately, when contamination is detected inside the battery cells, they are not fixable and must be discarded, which can be costly. Therefore, the earlier the contamination is detected, the more cost effective it will be.”
The best practice is to avoid contamination altogether by using non-ferrous metal-free components to ensure clean production during the battery cell manufacturing process. Festo supports battery manufacturers by offering a wide range of products that are free of copper, nickel, and zinc, the metals that can contaminate the battery cell during manufacturing. These products ensure a clean production process and high-quality batteries that benefit both the manufacturer and the customer.
Amid growing environmental challenges, industries around the world are adopting cutting-edge technologies to minimize their ecological footprint. Lin says that one of his key focus areas is supporting advancements in technologies that drive improvements in productivity, quality, and safety through innovative designs, especially the automation of battery production. “This critical aspect of the green revolution plays a vital role in shaping a sustainable future by enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and optimizing resource use in the production of batteries for EVs and energy storage systems.”
Automation solutions from Festo support the entire battery manufacturing process, from the cell to module production and insertion of the battery system. Their portfolio of products for producing batteries for EVs and energy storage systems prevents contamination from interfering particles, especially non-ferrous metals such as copper, nickel, and zinc. This ensures safe, quality batteries needed for a more sustainable future.
To know more visit Festo and if you enjoyed this article, you might also be interested in this free eBook.
Related Story
Battery Formation for EV Batteries: A Critical Step in Battery Production
Festo is a leading supplier of pneumatic and electrical automation technology, and they are supporting the Canadian automotive industry with innovative products, optimized motion control solutions, and unrivaled support. In this article, two subject matter experts from Festo, Jarod Garbe, Industry Segment Manager – Automotive, and Lawrence Lin, Emerging Technologies Business Development Manager -EV Batteries, shed more light on the subject. They discuss Festo’s products and solutions for EV battery production – with a particular focus on battery formation – arguably, the most critical part of the process.