Why Use VFD Cables? HELUKABEL Answers
January 6, 2023

Why Use VFD Cables? VFD cables are a critical component to extend a motor’s life cycle within a VFD system. Three areas where VFD cables set themselves apart from traditional tray-rated power cables are:
1. Address high and low frequency noise issues with proper shielding
Shielding on cables is what prevents systems from interacting with each other. In short, a cable’s shield is its defense against noise. THHN and most generic control/tray cables are constructed using either an aluminum shield or they are unshielded. HELUKABEL’s VFD cables are constructed using either a foil (100% coverage) + tinned copper braid (85% coverage), or a triple shield comprising of a semi-conductive fleece + foil + braid shield (80% coverage). Cables with the proper shielding prevent the VFD system from radiating electrical noise that can interfere with surrounding networking, instrumentation, wireless communication, and industrial devices.
2. Ability to withstand voltage spikes/reflected wave voltage
A cable combats voltage spikes with insulation material and wall thickness. HELUKABEL’s VFD cables use XLPE insulation as its conductor insulation. XLPE has a much lower capacitance (higher corona inception voltage) than THHN and generic control/tray cable which just use PVC. This is particularly important in wet or damp environments as PVC is more susceptible to absorbing moisture, which results in less than half the insulation capability of XLPE. The wall thickness of a VFD cable tends to be thicker allowing it to withstand voltage spikes significantly better.
The current NFPA guidelines require RHH, RHW, RHW-2, XHH, XHHE or XHHW-2 insulation for use inside the motor’s control panel or cabinet, but the expectation is this requirement will move to include cable used in external wiring of VFD applications in the upcoming years.
3. High temperature resistance
A cable’s type of insulation plays a significant role in how it responds to thermal stress. Thermoset insulation won’t melt or drip in higher temperatures like the thermoplastic insulation found in THHN and generic control/tray cables. If thermoplastic insulation is used, you run the risk that it will melt, drip, or simply deform, which reduces the insulation properties, and can cause damage to critical and expensive equipment/machinery.
UL/CSA VFD Cable Products
TOPFLEX®
XLPE Insulation, EMC-preferred Type, Flexible Motor Power Supply Cable, Oil-resistant, NFPA 79 Ch. 4
XLPE Insulation, EMC-preferred Type, Flexible Motor Power Supply w/ Control Conductors, Oil-resistant, NFPA 79 Ch. 4
XLPE Insulation, EMC-preferred Type, Flexible Motor Power Supply w/ 3 Symmetrical Ground Conductors, Oil-resistant, NFPA 79 Ch. 4
TOPSERV®
XLPE Insulation, EMC-preferred Type, Highly Flexible Motor Power Supply Cable, Oil-resistant, NFPA 79 Ch. 4
XLPE Insulation, EMC-preferred Type, Highly Flexible Motor Power Supply w/ Control Conductors, Oil-resistant, NFPA 79 Ch. 4
Complete Your Cable System
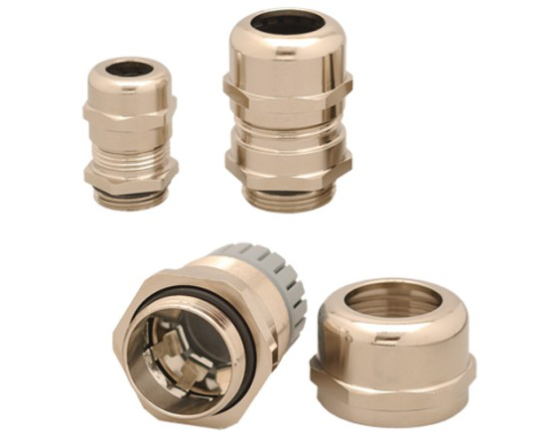

Further enhance your electric motor’s lifespan by using EMC glands to protect your equipment from electromagnetic interference. EMC glands perform a key function in EMC protection by deflecting electromagnetic waves over the housing surface at a critical transition point – entry into the enclosure – in order to protect the exposed cables inside.
Thanks to their enlarged contact surfaces, EMC cable glands improve conductivity between the cable shield and gland on the enclosure housing. With their copper beryllium contact system, products such as the HELUTOP® MS-EP and MS-EP4 ensure excellent shielding attenuation and current dissipation. Contact is made automatically when the gland is tightened, and the polyamide PA 6 insert provides perfect strain relief.
Put to the Ultimate Test Cables and wires in industrial robots and other moving machine parts are often required to withstand extreme stresses caused by torsion. Find out how HELUKABEL puts their cables to the ultimate test. Read Part 1: Torsion Tests by HELUKABEL